Starbucks, the American global coffee giant, is currently facing major pressure in the domestic market ahead of its latest earnings report. The company is expected to report its sixth consecutive quarterly sales decline in the U.S., reflecting serious challenges in maintaining relevance and appeal amid shifting consumer behaviors and internal operational dynamics.
Since taking over as CEO in September 2024, Brian Niccol has launched a series of ambitious transformation efforts under the “Back to Starbucks” strategy. His primary focus is to restore Starbucks’ essence as a “third place”—not merely a spot to buy coffee, but a social and community hub. Niccol acknowledged that previous decisions had eroded this character, such as removing customer seating and overly complicating the menu.
In response, Starbucks has cut approximately 30% of its U.S. menu items, including 13 less popular drinks. The goal is to simplify operations, speed up service, and reduce barista workload. The company also aims for a maximum order preparation time of 4 minutes, utilizing new queue algorithms and staff retraining programs.
These improvements extend beyond just the kitchen and quick-service model. Starbucks also announced plans to renovate 1,000 stores in the U.S. with more comfortable, community-oriented designs, starting with a pilot location in Bridgehampton, New York. Over 10,000 outlets will also be reinforced with additional staffing during the summer, especially to accommodate growing digital orders.
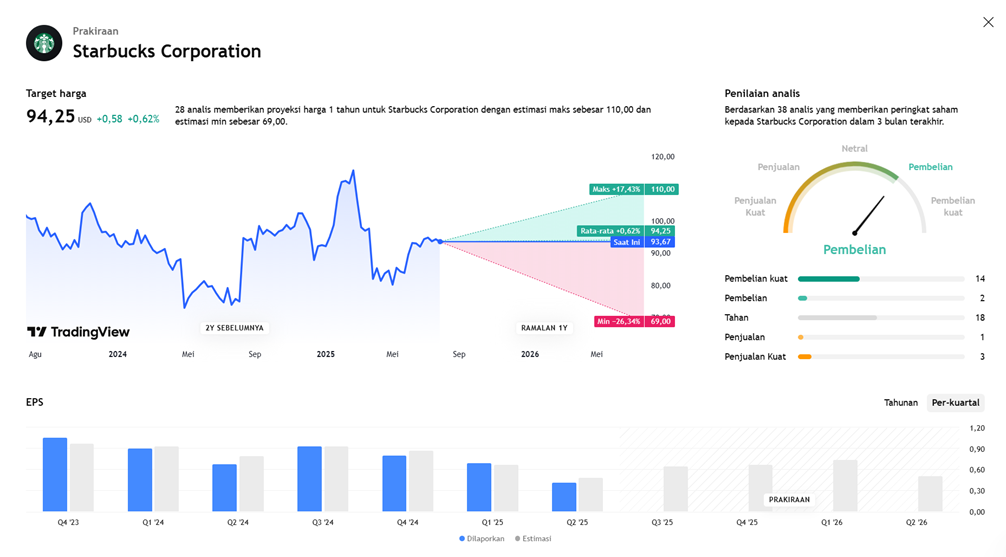
While this transformation reflects a strong long-term vision, Wall Street has begun expressing doubts. Starbucks’ stock did surge around 28% when Niccol was named CEO, but it has since come under pressure due to concerns about the effectiveness of the strategy and the high transformation cost—estimated between USD 1.5 billion and 2 billion over the next two years. Analysts and investors are also uneasy about the company’s lack of updated financial guidance or annual revenue forecasts, which adds to uncertainty about the business direction.
Overall, Starbucks stands at a critical crossroads. The comprehensive turnaround strategy under Brian Niccol shows a serious commitment to repositioning the company, but the still-negative short-term results suggest that recovery won’t happen overnight. The biggest question going forward: are consumers—and investors—willing to give Starbucks the time it needs to bounce back?
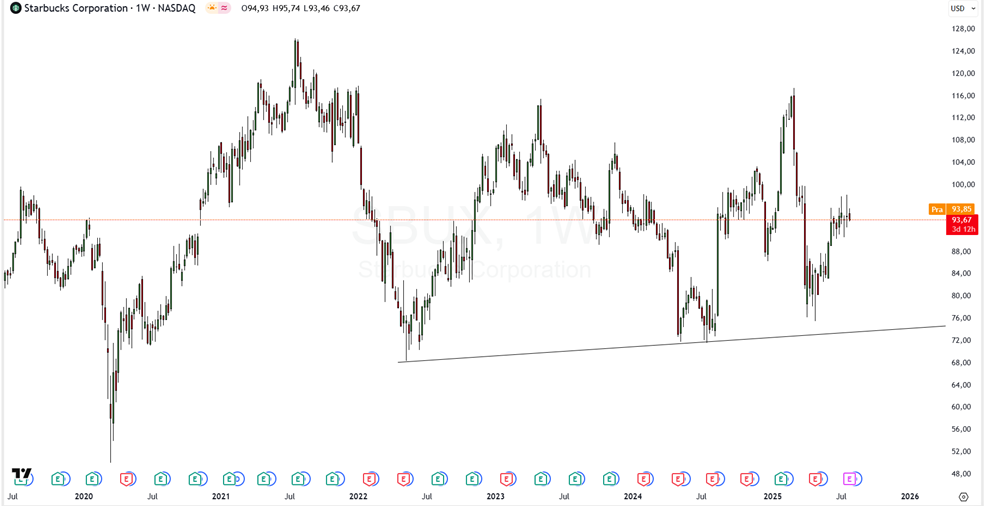
Q3 2025 Financial Performance Forecast
- Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- Consensus Estimate: $0.64–$0.65
- Decline: ~31% from Q3 last year ($0.93)
- Jefferies’ view (more pessimistic): $0.53, expecting margin pressure from high costs and weak transaction volume
- Earnings ESP +1.20% → this combination does not support a strong earnings beat potential
- Implication: If actual EPS falls below $0.64, markets are likely to react negatively, as this would reflect that turnaround efforts have not offset cost pressures and weak consumer demand.
- Revenue
- Projection: $9.29 billion
- YoY Growth: +1.9%
- Drivers:
- New store openings
- Investment in digital & mobile orders
- Seasonal menu & product innovation
- However, growth is limited by stagnation or decline in same-store sales, particularly in the U.S., Starbucks’ largest market.
Key Performance Drivers
- Operational Transformation: Green Apron & Streamlined Menu
- Starbucks simplified its menu by 30%, eliminating slower-to-prepare drinks to speed up service and reduce barista burden.
- The Green Apron model adds specialized staff to handle digital orders more quickly, improving customer experience.
- However, this strategy adds significant costs. Labor expenses in U.S. stores are projected to rise by up to 12%.
- Digital & Customer Loyalty
- Starbucks continues expanding digital ordering and its loyalty program as key growth drivers.
- The focus is now shifting to in-store customer experience with a more personal approach, acknowledging that many customers are “switching from out-of-home to in-home coffee” due to pricing and inflation.
- Margins & Costs
- Operational costs are rising, particularly from:
- Worker wages
- Raw material inflation (coffee, milk, energy)
- Chinese import tariffs (digital equipment & store machinery)
- Margins are expected to shrink compared to last year, as higher costs are not yet fully offset by higher volume or average selling prices.
- Operational costs are rising, particularly from:
Market Risks & Concerns
- Negative Comps
- Same-store sales in the U.S. are expected to remain negative, following a -3% trend in Q2.
- Customer visits to physical stores have not yet returned to pre-pandemic levels, particularly in urban areas.
- China: Second-Largest Market Remains Sluggish
- Post-COVID reopening in China has not resulted in steady sales recovery.
- Geopolitical uncertainty and domestic economic slowdown in China pose additional global risks for Starbucks.
Market Commentary & Analyst Views
- Jefferies: Downgraded SBUX to Underperform, citing overly optimistic valuation and risks from a capital-intensive and time-consuming transformation.
- Bulls (Optimists): Some analysts believe the “Back to Starbucks” strategy will yield visible results starting in H2 2025, supported by store redesigns, menu innovation, and loyalty program expansion.
- Bears (Skeptics): Others are concerned Starbucks is “overinvesting in the future” without clear short-term returns. Vague guidance and declining EPS remain key concerns.
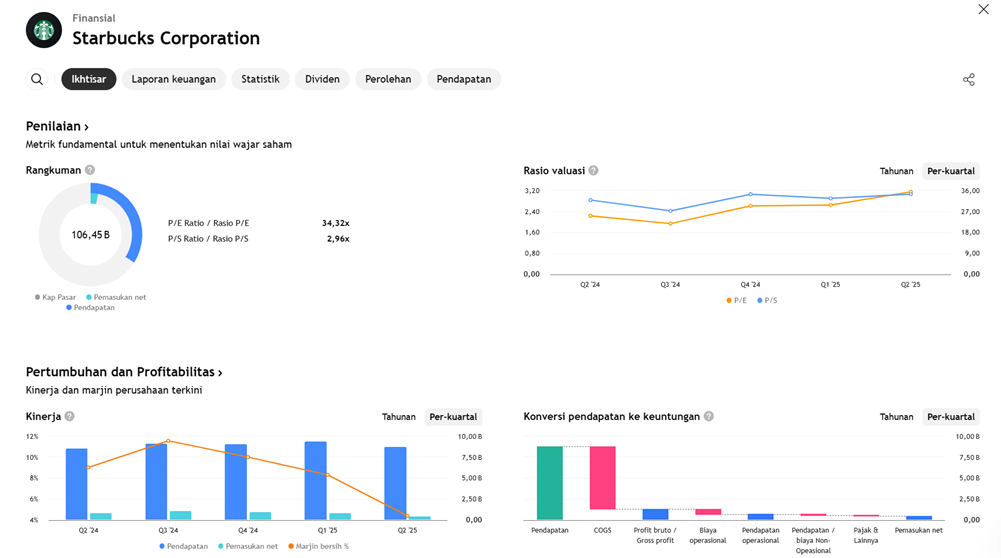
EARNING PROJECTION PREDICTION
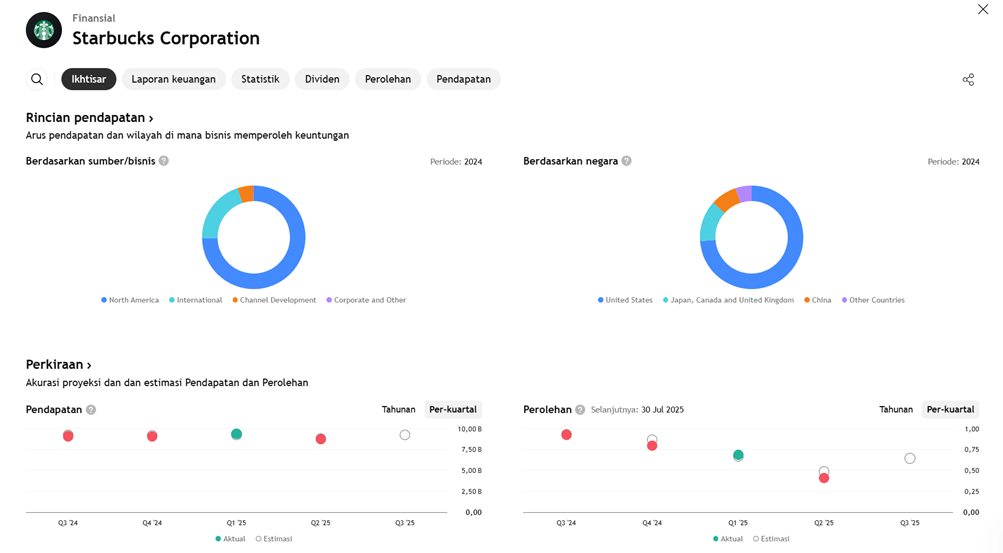
WHAT THE ANALYST STATED